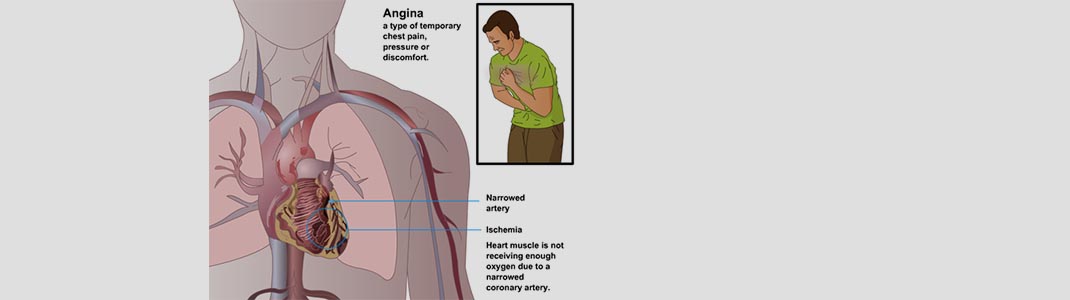
INTRODUCTION —Angina pectoris, or angina for short, is the term used when chest discomfort is thought to be attributable to reduced blood supply to the heart. In patients with angina, chest discomfort is often but not always present. Other associated symptoms of angina include exertional shortness of breath, nausea, sweating & fatigue. This has been termed “silent angina “.
Ques Why does angina occur?
Ans: Angina occurs because the arteries supplying blood to the heart are blocked. Sometimes there can be other causes of angina such as abnormality in the heart structure or change in the rhythm of heart
Ques Where does the pain of angina occur?
Classic angina pectoris is described as a pressure, heaviness, tightness, or constriction in the center or left of the chest that is precipitated by exertion and relieved by rest.
How does angina pain feel?
Angina is usually characterized more as a discomfort rather than pain. Terms frequently used by patients include squeezing, tightness, pressure, constriction, strangling, burning, heart burn, fullness in the chest, bandlike sensation, knot in the center of the chest, lump in throat, ache, heavy weight on chest (elephant sitting on chest) .In some cases, the patient cannot qualify the nature of the discomfort, but places his or her fist in the center of the chest.
Angina is typically gradual in onset and offset, with the intensity of the discomfort increasing and decreasing over several minutes
Generally, it is felt in the same location.
Angina is a constant discomfort that does not change with respiration or position.
Sometimes angina often radiates to other parts of the body, including the upper abdomen (epigastric), shoulders, arms (upper and forearm), wrist, fingers, neck and throat, lower jaw and
teeth (but not upper jaw), and rarely to the back (specifically the interscapular region) .
Radiation to both arms is a stronger predictor of acute myocardial infarction.
What can provoke angina − Angina is often elicited by activities and situations that increase myocardial oxygen demand, including physical activity, cold, emotional stress, sexual intercourse, meals.
Meal pain is generally considered to be gastrointestinal in origin. However, it may also be anginal, especially in patients with severe ischemia.
Angina occurs more commonly in the early hours of morning
How long the pain of angina last − Classic angina is often relieved with termination of the provoking factor. Angina generally lasts for two to five minutes.
Other symptoms may include belching, nausea, indigestion, diaphoresis, dizziness, lightheadedness, clamminess, and fatigue. However, these symptoms may be seen with other etiologies for chest pain, especially gastrointestinal causes.
The diagnosis of myocardial ischemia can often be made with a high degree of certainty based on the history, physical examination, and electrocardiogram. Such patients have classic angina, either a normal physical examination or features consistent with myocardial ischemia, and an electrocardiogram that is normal in the absence of ongoing ischemia. Some patients may require stress testing for the purpose of diagnosis, but in most cases it is performed for prognostic reasons.
020 2634 2998 | 020 4862 2074
INFO@MARIANHEART.ORG